Protein Processing I: Targeting to the Endomembrane System
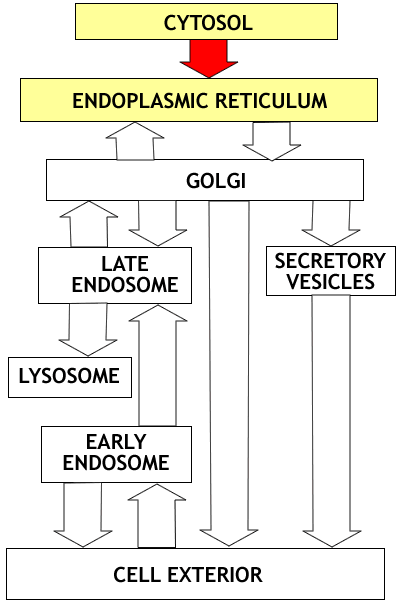 |
Overview of the Endomembrane System:The
Endomembrane system is a complex of membrane limited compartments involved
in the processing and movement of proteins. Newly synthesized proteins
enter the endomembrane system through the endoplasmic reticulum. From
there them move through the Golgi apparatus and into either the Secretory
Pathway or the Lysosomal Pathway.
We begin by looking at targeting of proteins from the
cytosol to the endoplasmic reticulum.
|
1. Targeting to the endoplasmic reticulum.
Synopsis.
Synthesis of proteins entering the endoplasmic reticulum is
initiated on free ribosomes.
A targeting sequence of hydrophobic amino acids near
the N- terminal end of the growing polypeptide results in the binding of the
ribosome to ER membrane and in insertion of the polypeptide into the endoplasmic
reticulum.
Proteins going to Golgi, endosomes, lysosomes and ER all enter
the ER and don't come out again.
Two groups of proteins are targeted to the ER:
- Proteins that are completely translocated into lumen of the
ER. These are soluble proteins destined for secretion, or for the lumen
of another organelle. These proteins are never part of membranes.
- Proteins that are inserted into membranes, and hence are
only partially translocated into the endoplasmic reticuluum. These proteins
may be destined for ER, another organelle, or the plasma membrane. In
all of these cases the proteins stay within the membrane (e.g. cellulose
synthase).
Let's deal first with the case of proteins that will be
inserted into the ER lumen:
- The signal sequence is a long sequence of about 20 hydrophobic
amino acid residues that contains a hydrophobic membrane crossing domain at
the N terminal end.
- The emerging signal sequence combines with a 'signal
recognition particle' (SRP). This greatly reduces the rate of translocation
and allows the ribosome to attach to the endoplasm reticulum by means of a
special SRP receptor in the ER membrane.
- The ribosome becomes attached to a ribosome receptor
that also functions as the translocation channel for the
newly synthesized polypeptide. As the ribosome becomes attached, the SRP is
removed and translation resumes.
- The protein is fed through the translocation channel.
- After translation is complete, the signal sequence, which
is embedded into the ER membrane, is cleaved off of the protein by a specific
signal peptidase, an enzyme that is present in the ER lumen.
- This leaves the newly synthesized protein free in the lumen
of the ER.
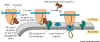 Figure 14-13.
Figure 14-13. |
Animation
of co-translational insertion of protein into lumen of ER |
Proteins inserted into membranes:
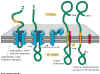
Figure 14-15.
Animation
of insertion of a single pass membrane protein with N terminal end in
ER lumen
|
Import of a membrane protein into the membrane
of the ER. The blue sheath-like component shown in the figure is the translocation
channel that moves the protein through the membrane. Notice that the Stop
Transfer sequence (orange) results in the disassembly of the translocation
channel. Note that the signal sequence at the N terminal end of the protein
is cleaved off, releasing the N terminal portion of the protein into the
ER lumen. This example is a single pass membrane protein that contains
a single membrane crossing domain (the stop transfer signal). |
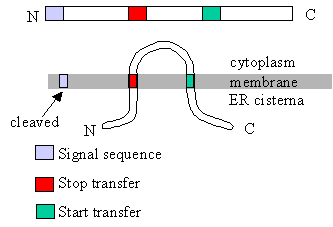 |
This diagram shows the relation between translocation
control sequences (signal sequences, start transfer sequences, stop transfer
sequences) and the arrangement of the protein in the membrane.
How would the translocation control sequences have to
be arranged to get the N terminal end of the protein on the cytoplasmic
side? - to get the C terminal end of the protein on the cytoplasmic side?
|
Link to animations
of co-translational insertion of proteins (5 different cases).


